EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN PUPPIES
Hip Dysplasia in dogs is an anatomical orthopedic condition which has a genetic background and affects mostly large breeds. Dogs with severe degree of hip dysplasia develop osteoarthritis and pain as they are ageing.
For this reason an early detection of this condition might be a great gift for your little one especially if it takes place around the time of its second puppy vaccine.
Usually at this age dogs with hip dysplasia do not show symptoms so an x-ray screening with the use of a distraction device (Penn-Hip method) is necessary. This device permits the accurate measurement of maximum hip laxity, which means the distance the ball (femoral head) can be displaced from the hip socket (acetabula) and is called Distraction Index (DI). DI higher than 0.3 and lower than 0.5 reveal good surgical candidates for a minimal surgical technique called JPS – Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis. This surgical technique which is even less invasive than a spay surgery can be performed only in puppies up to 4 months of age when the growth plates of their pelvis are still open.There is about 85% chance that predisposed to Hip Dysplasia dogs will benefit from having the procedure done strictly at this age (12 -16 weeks).
The pictures of the pelvis (before and after JPS) illustrates how this technique works.
The center of the pubic bone (arrow) is destroyed gently with electrocautery, so that this part of the pelvis will no longer grow. The other parts of the pelvis though keep on growing normally having as a result a better coverage of the acetabulum (socket) over the femoral heads (balls).
recent post

EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN PUPPIES
Hip Dysplasia in dogs is an anatomical orthopedic condition which has a genetic background and affects mostly..
learn more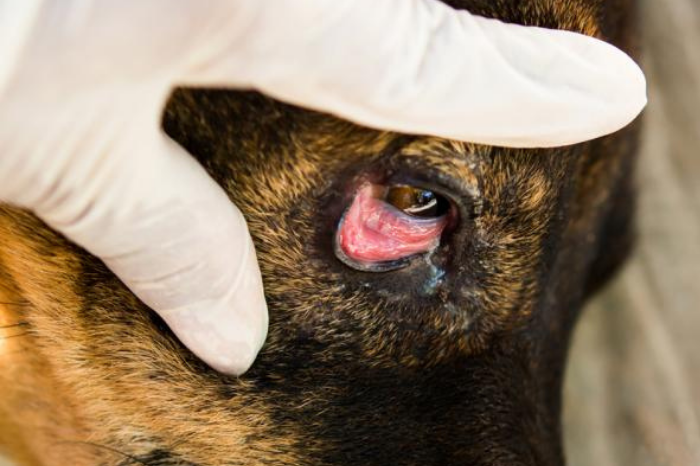
“CHERRY EYE” or PROTRUSION OF THE GLAND OF THE 3rd EYELID
Protrusion of the gland of the third eyelid (or “cherry eye”) occurs most commonly in dogs and..
learn more